Fossil: (noun)
The remains or impression of a prehistoric plant or animal embedded in rock and preserved in petrified form.

Palaeontology: (noun)
The branch of science concerned with fossilized animals and plants.
Paleontology In India:
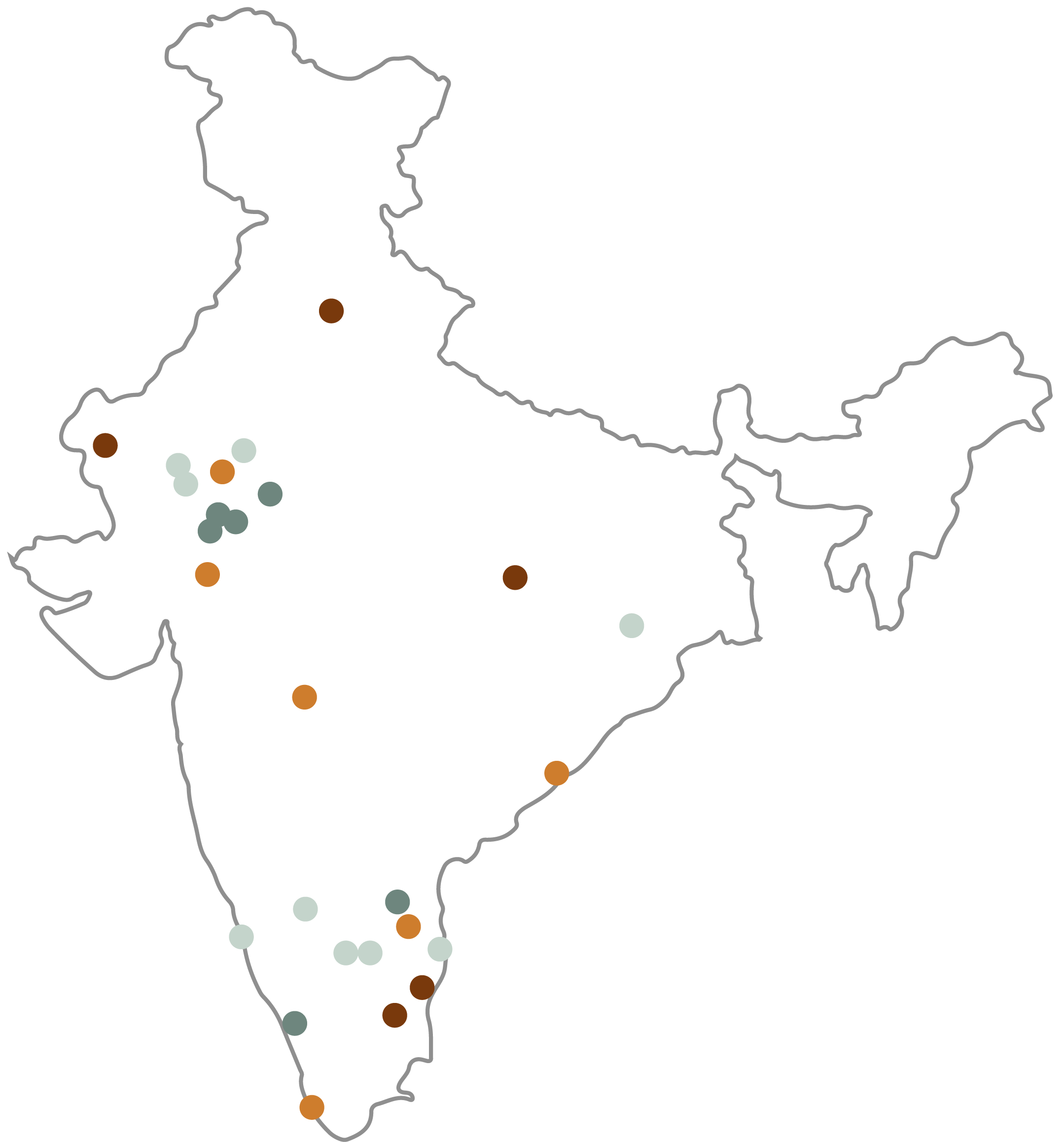
In India, fossil sites fall under the category of Geological Heritage. The most prominent authority for the protection and study of these monuments and other geological resources is the Geological Survey of India. As of 2016 there were 26 Geological Monuments in India each managed by the GSI.
However, apart from declaring sites as Geological Monuments, no framework or policy exists for the protection of fossil sites. Hence, the sites lie in deplorable conditions being neglected for long periods of time without maintenance.

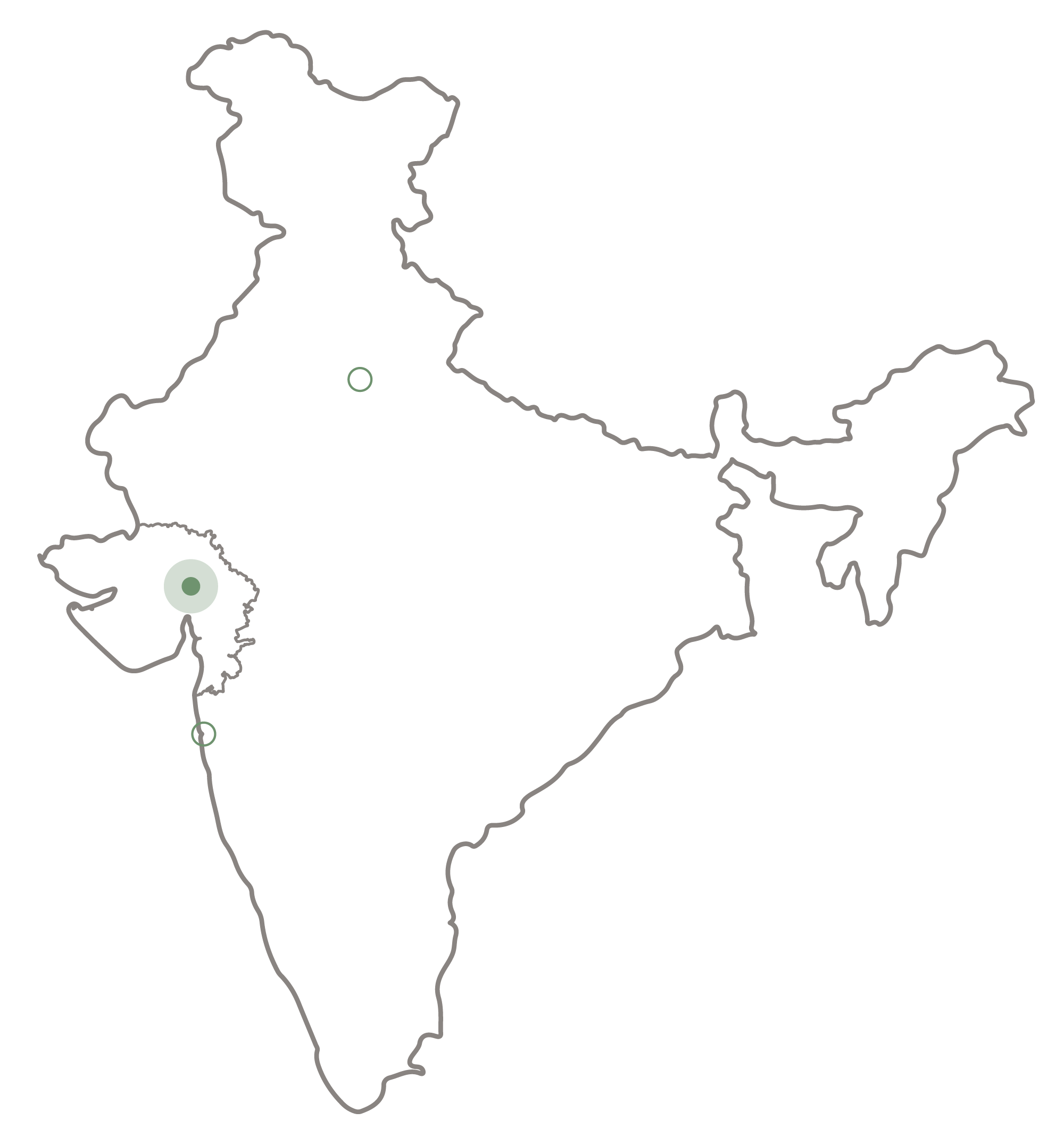
The Balasinor (Raiyoli) Fossil Park, located around 90 km to the East of Ahmedabad in the
Mahisagar district of Gujarat. Raiyoli is placed prominently on the world palaeontological
map as it is one of the best places in the world to see dinosaur nests and eggs.
After its ‘accidental’ discovery, many more dinosaur eggs were found throughout Gujarat,
Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh by the GSI. However, Raiyoli still remains the largest and
most prominent dinosaur nesting ground discovered in India and perhaps in the world. Sadly,
as soon as the news about the findings spread, the site was looted and vandalized with
several specimens being removed by vandals.

The System: Arriving at a Solution.
Given the political and academic predicaments that paleontology is facing, the thesis aimed to develop an alternate approach for the field.
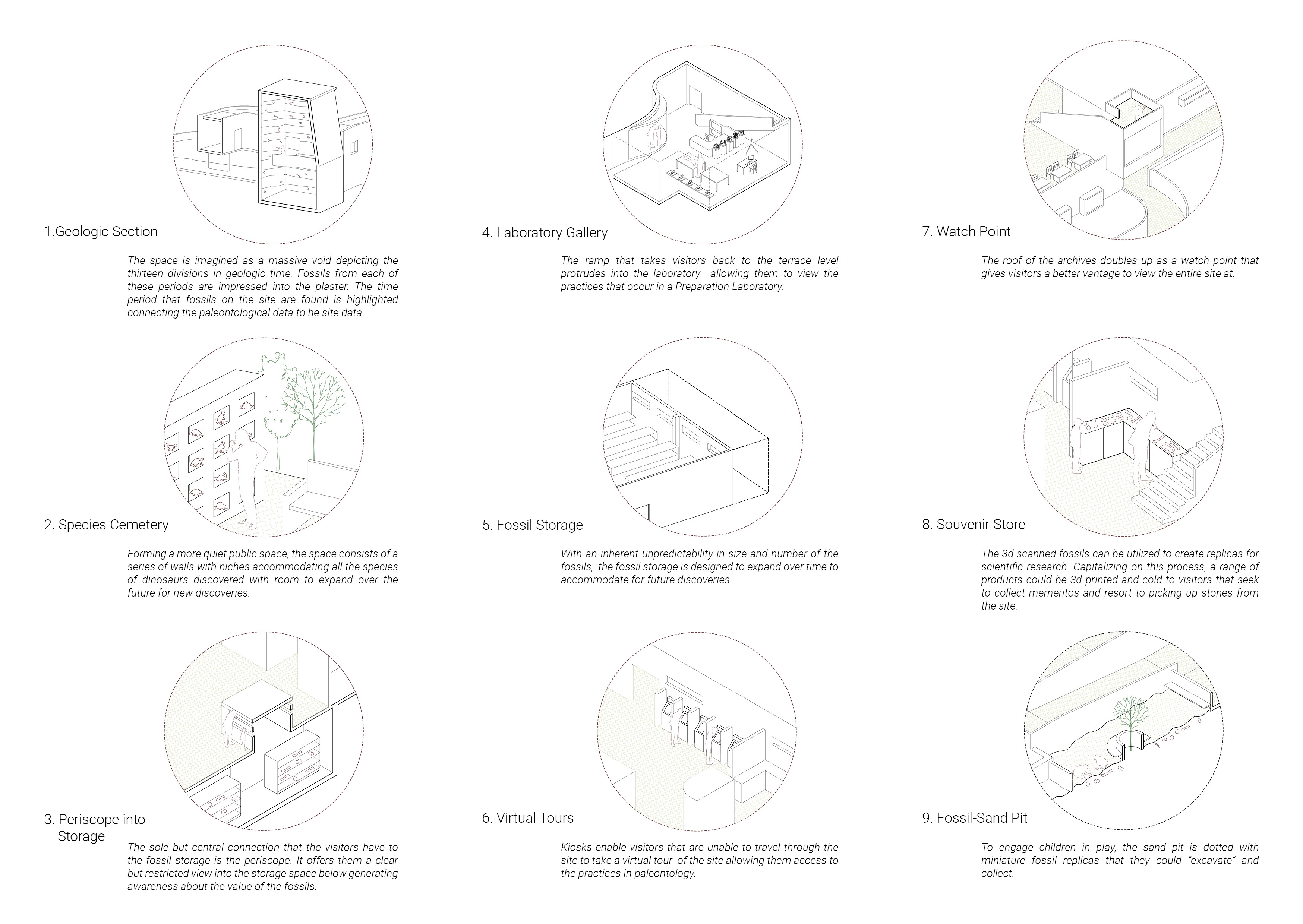
By looking at case studies, frameworks and programmes that exist internationally, a system was amalgamated that would aid the propagation of knowledge and interest about fossils and simultaneously protect the valuable scientific resources.
The system developed, utilizes existing processes within the field of paleontology to generate an interest among visitors and also aid the site financially.

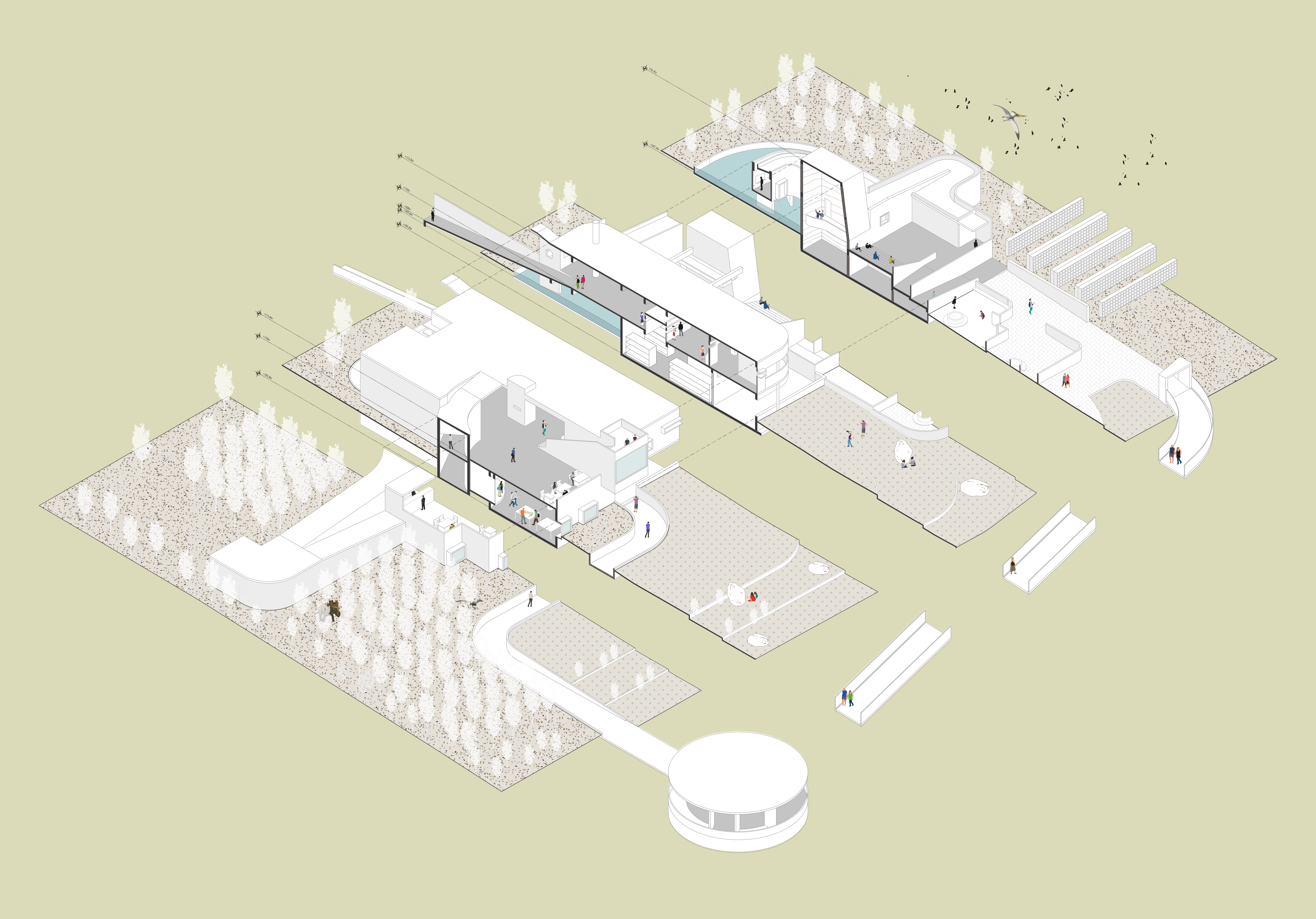
Ex-Situ Facility:
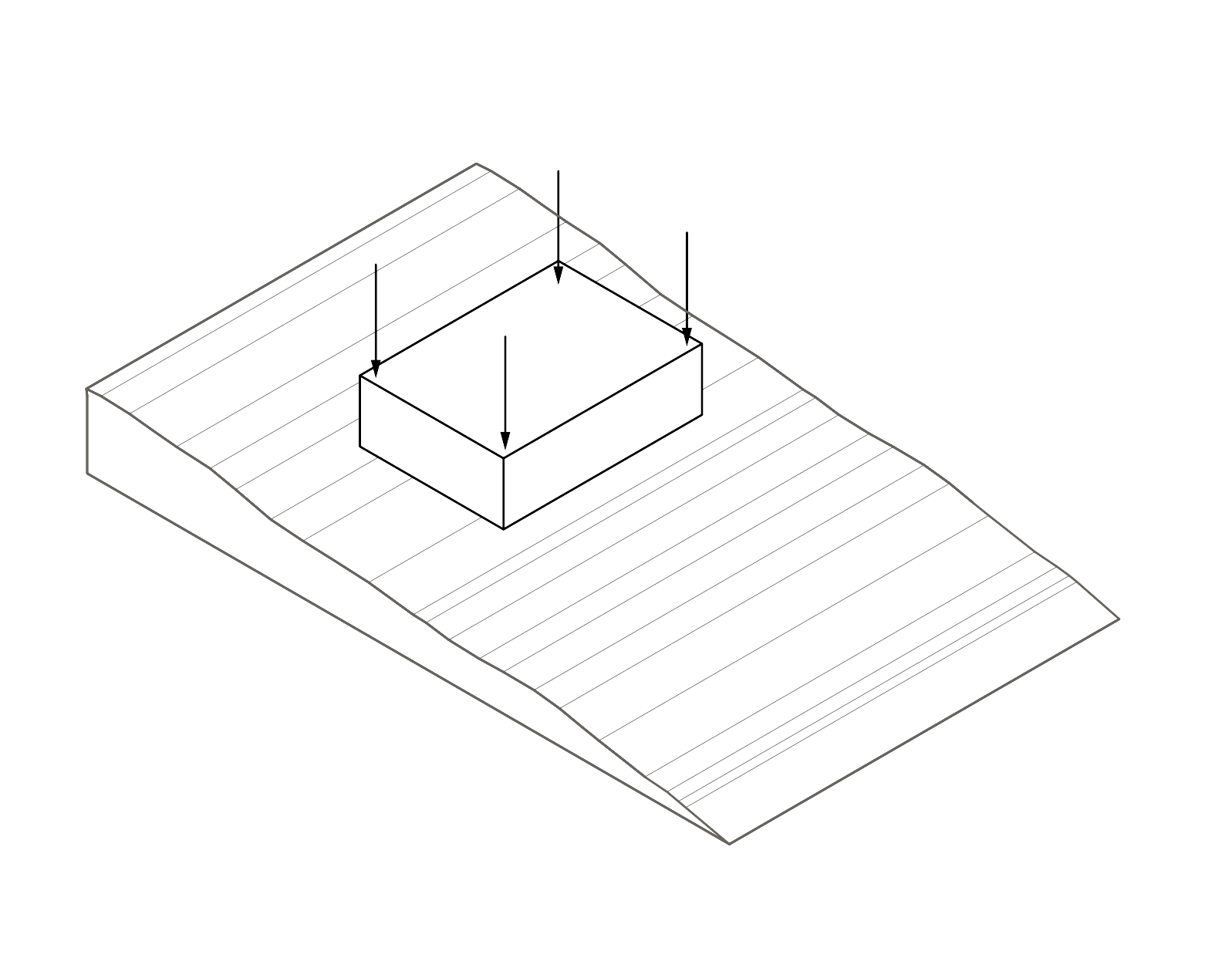
After studying the process a fossil goes through from the time of its extraction, one realizes that the need of a permanent, well equipped facility exists to prepare and store the fossils. However, this facility has to be sited bearing in mind that no further damage is caused to the fossils buried under the surface.
During the process of uplift and erosion, gravity causes the fossils to gradually move downhill. Hence, a great number of fossils are discovered on cliff faces or bottoms. Due to the comparatively higher chances of finding fossils near the low lying areas, the facility would have to be sited away from these regions.
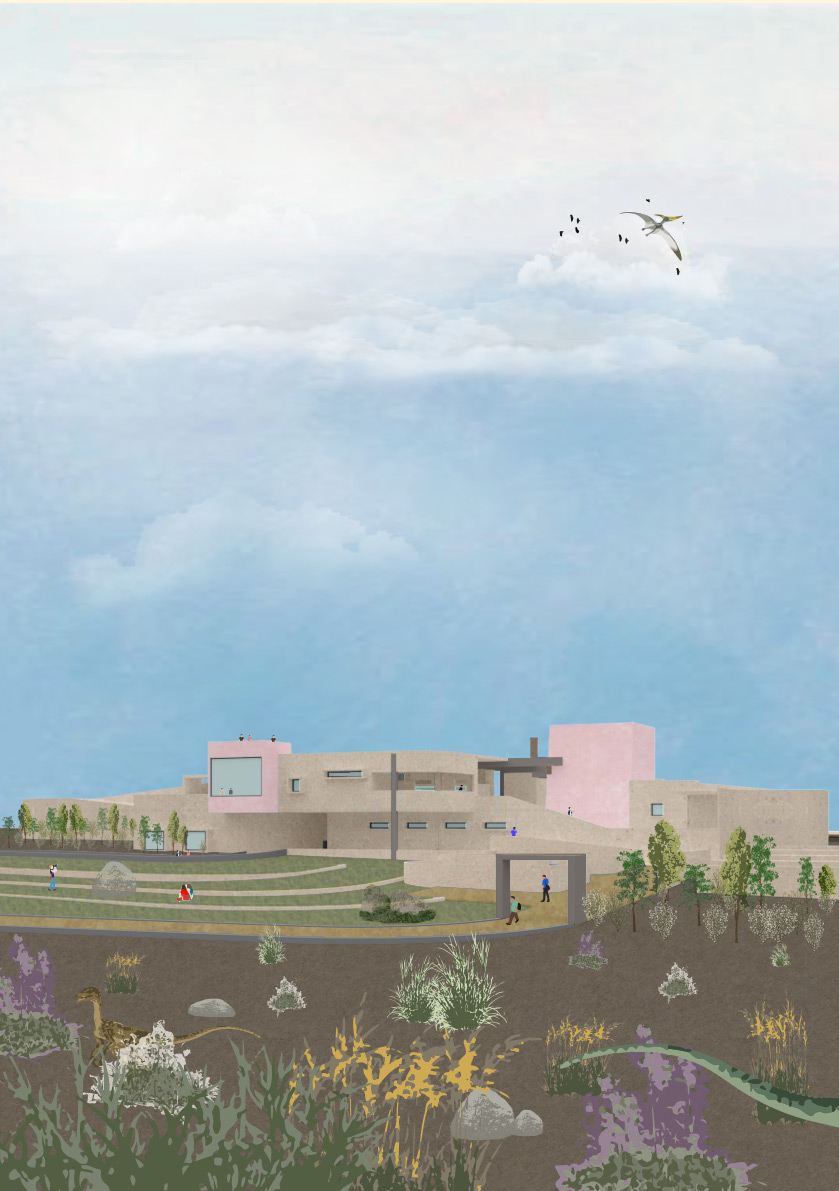
The abandoned nursery was selected as the site of intervention due to its higher elevation, proximity to the road and alternate land use. Further, any fossils that may have existed below the nursery are likely to be highly damaged due to the roots of the trees that once grew there.
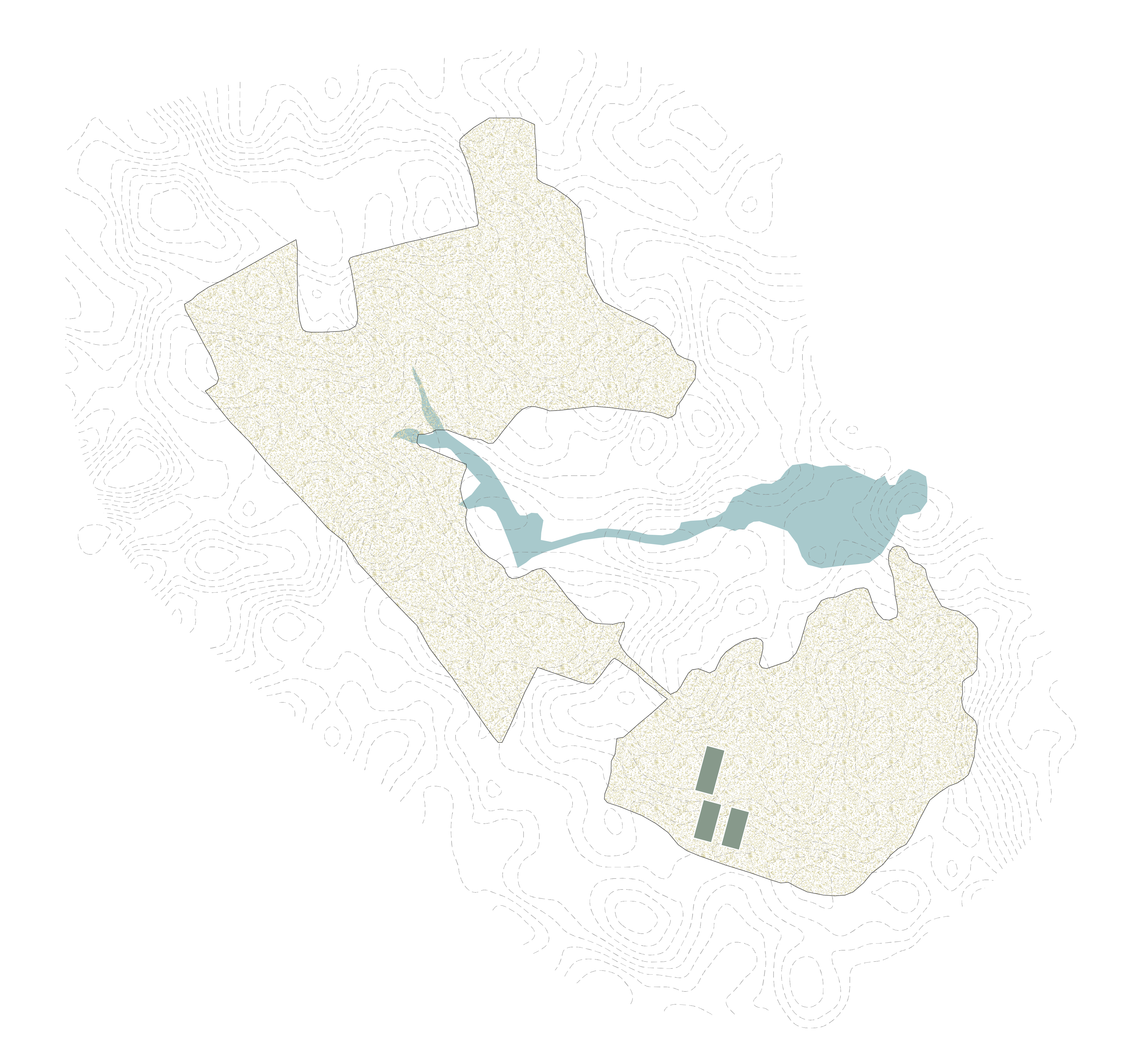
The essential functions of the fossil storage, preparation laboratory and the appropriate services are partially sunken within the earth. This reduces dependency on mechanical air conditioning systems to maintain the temperature of these spaces.
The public functions are located above these submerged spaces reducing the footprint of the structure, further insulating the space below and providing the visitors with a moderate vantage to view the rest of the site at.